Position size is a crucial component of trading that many traders often overlook. It refers to the amount of a particular asset a trader is willing to invest in a single trade. Correctly calculating and managing position size is essential to effectively managing risk and maximizing profits. This article will explore what position size means, how to calculate it, and why it is necessary.
What is Position Size?
Position size is the number of units of a particular asset a trader is willing to buy or sell in a single trade. It is usually expressed in lots, shares, or contracts, depending on the asset being traded. For instance, a trader buying 100 shares of a stock is taking a more significant position size than a trader buying 50 shares.
Calculating Position Size
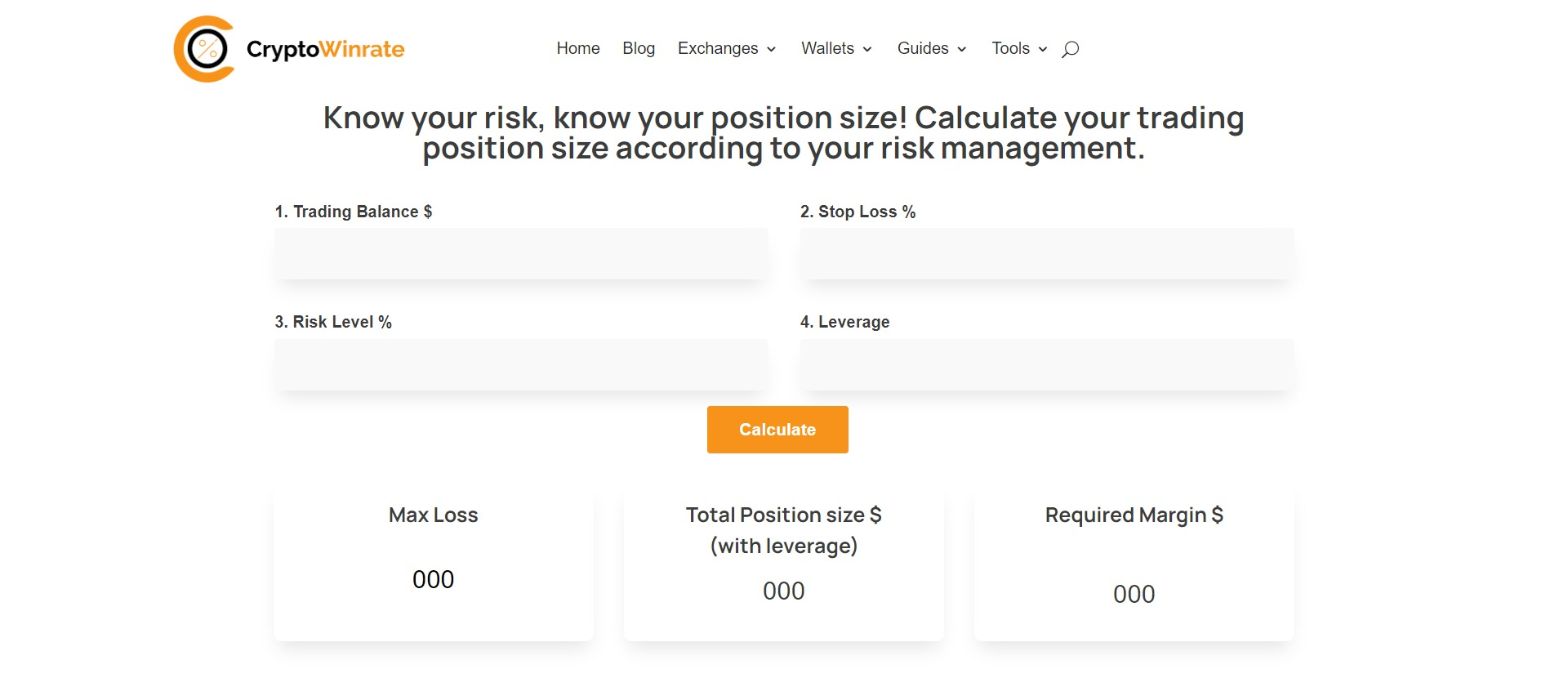
To calculate your position size, you need to consider your balance, the level of stop loss, and the risk percentage. A widely used formula is:
Position size = (Account balance x Risk percentage)/Stop loss distance
For instance, if your account balance is $10,000, and you’re willing to take a chance of 2 percent of your fund on trading activities with a stop-loss order of 50 pips, its position size will be:
Position size = (10,000 x 0.02)/50 = 4 lots
Why is Position Size Important?
Position size is an essential component of trading that determines the amount of a particular asset a trader is willing to buy or sell in a single trade. Properly calculating and managing position size is crucial for traders to manage their risk effectively and maximize their potential profits.
Risk Management
One of the most critical reasons for managing position size is risk management. By taking too large a position size, traders expose themselves to significant risk. If the trade goes against them, they risk losing a considerable portion of their trading account on a single trade. On the other hand, taking too small a position size may limit potential profits. Properly calculating and managing position size can help traders manage their risk effectively, ensuring they only lose what they can afford on any single trade.
Maximizing Profits
While risk management is crucial, traders also want to maximize their profits. By selecting the appropriate position size, traders can ensure that they make the most of profitable trades while limiting their risk. Properly managing position size can help traders maximize their potential profits while minimizing losses.
Consistency
Properly managing position size can help traders maintain consistency in their trading. Consistency is crucial to success in trading. By selecting an appropriate position size, traders can keep a consistent approach to trading, ensuring their risk management strategy is consistent across all their trades.
Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
Properly managing position size is also vital in adapting to changing market conditions. Market conditions can change rapidly, and traders need to be able to adjust their position size accordingly. For example, during high volatility, traders may need to reduce their position size to manage their risk effectively.
When to Increase Position Size?
Here are some scenarios in which traders may consider increasing their position size:
Increased Confidence
If a trader is consistently profitable and has developed a successful trading strategy with a good winrate, they may consider increasing their position size. This should be done gradually based on the trader’s confidence in their approach.
Positive Market Conditions
If the market conditions are favorable, and the trader has identified a trend likely to continue, they may consider increasing their position size. However, traders should be cautious and make changes gradually, taking into account the potential risks.
Increasing Account Size
As a trader’s account size grows, they may consider increasing their position size. However, this should be done gradually, and traders should ensure that their risk management strategy remains consistent.
Diversification
Traders may consider increasing their position size in a particular asset if they are diversifying their portfolio. Diversifying their portfolio allows traders to manage risk effectively and potentially increase their profits.
High Reward-to-Risk Ratio
If a trade has a high reward-to-risk ratio, traders may consider increasing their position size. However, they should be cautious and ensure that their risk management strategy is consistent.
What is a Good Position Size?
A good position size is one that allows you to limit your risk to a predetermined amount. A commonly used rule of thumb is to never risk more than 1% of your account balance on a single trade. This means that if you have a $10,000 trading account, you should not risk more than $100 on a single trade.
Another essential factor to consider is the stop loss level. Your position size should be adjusted to ensure that your stop loss level is appropriate for the market conditions. If the stop loss level is too close, you risk getting stopped out prematurely. You risk losing too much on a single trade if it’s too far away.
In general, a good position size is one that allows you to stay within your risk tolerance while also providing the potential for significant profits. A position size between 0.5%-5% of your account balance is generally considered reasonable, with 1% being the ideal amount.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding position size is critical for any trader looking to succeed in the markets. Traders can effectively manage risk and maximize profits by properly calculating and managing position size. It’s essential to stay within your risk tolerance, adjust your position size according to market conditions, and use stop losses to limit your losses. With a proper position size, traders can improve their chances of success in the markets. Remember always to take a cautious approach to risk management and never invest more than you can afford to lose.