The blockchain industry continues to redefine how financial systems operate, introducing innovative mechanisms to overcome persistent challenges in decentralized finance (DeFi). One such innovation is Proof of Liquidity (PoL)—a concept aimed at tackling the liquidity constraints often encountered in crypto ecosystems.
In blockchain networks, liquidity is vital, determining how easily assets can be traded without significant price volatility. However, traditional liquidity solutions often involve centralized market makers, which can lead to inefficiencies and vulnerabilities. Proof of Liquidity presents a decentralized alternative, addressing liquidity shortages while ensuring ecosystem security and functionality.
In this article, we’ll explore what Proof of Liquidity is, how it differs from other models, and its potential to revolutionize the way blockchain networks handle liquidity.
What Is Proof of Liquidity Mechanism (PoL)?
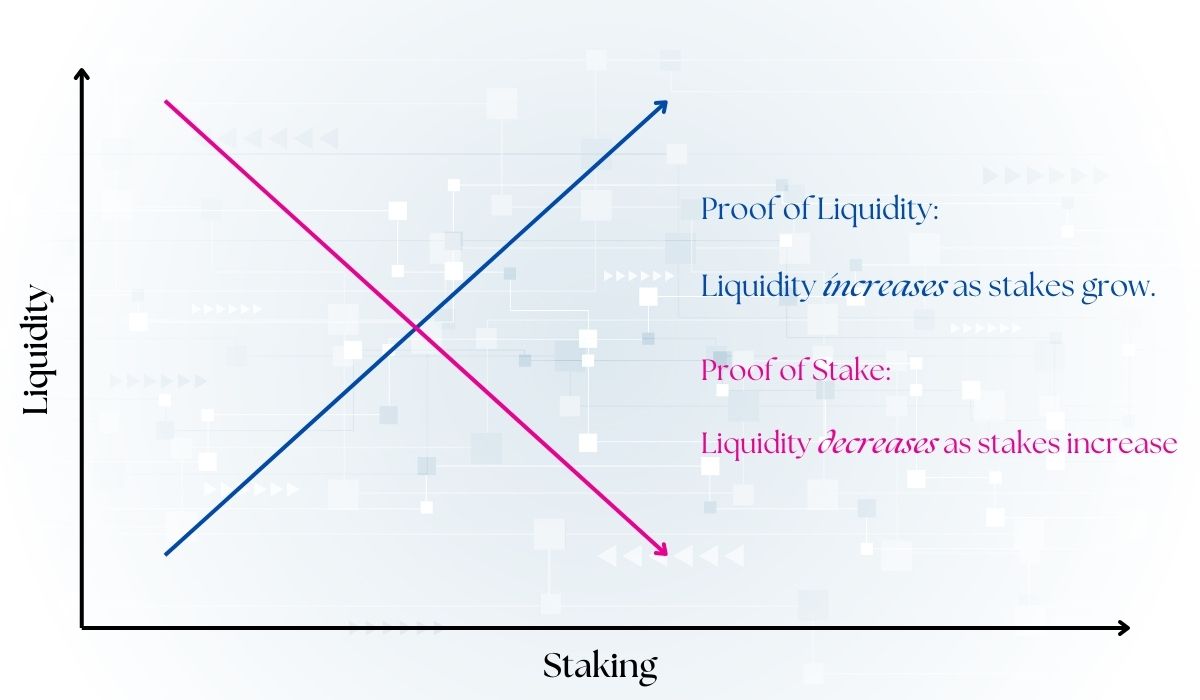
In current PoS systems, users stake their tokens to secure the network. However, these staked tokens become locked, rendering them unusable within the ecosystem. This leads to liquidity constraints, as staked assets cannot be leveraged for other purposes, such as trading, lending, or ecosystem activities.
Additionally, there is a structural value mismatch between validators and protocols in PoS systems:
1. Protocols drive ecosystem growth and activity but cannot contribute directly to network security.
2. Validators, who provide infrastructure and network security, gain limited benefits from the protocols they support. Their primary rewards come from transaction fees, leaving minimal incentive alignment between the two.
Proof of Liquidity seeks to overcome these challenges by introducing mechanisms where staked tokens can remain liquid and actively contribute to the ecosystem while still securing the network. It promotes a more synergistic relationship between validators and protocols, ensuring both parties benefit more equitably from their roles in the ecosystem.
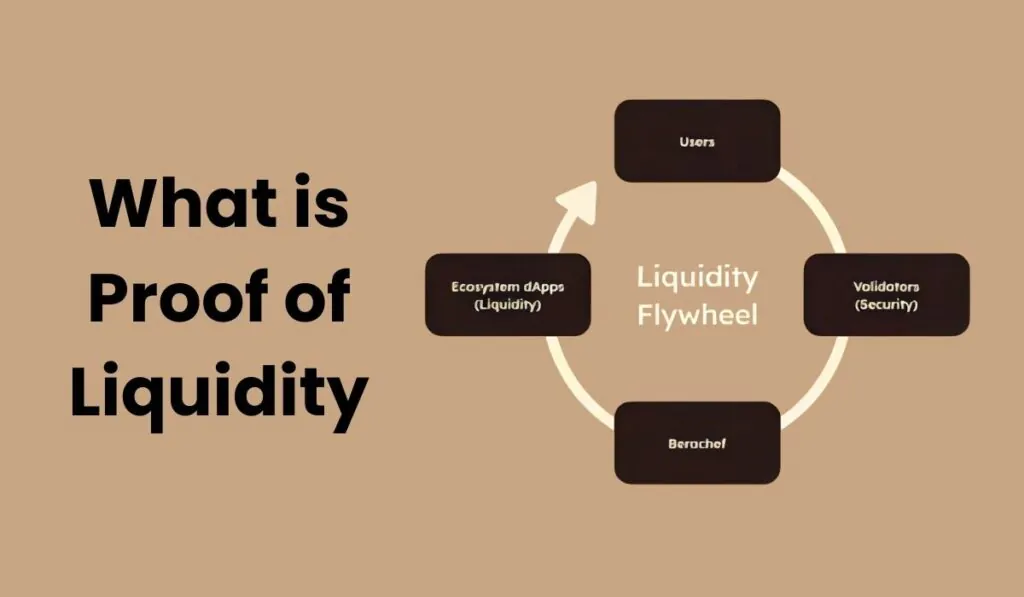
Berachain’s Proof of Liquidity
Berachain has introduced an innovative approach to liquidity management by utilizing Proof of Liquidity (PoL) as its core consensus mechanism. Unlike traditional Proof of Stake (PoS) or Proof of Work (PoW) systems, PoL focuses on enabling liquidity to remain fluid and accessible while still securing the network. This model not only decentralizes liquidity management but also directly incentivizes users by providing rewards for contributing to liquidity pools.
At the heart of Berachain’s implementation is the integration of liquidity providers into the network’s security layer, a concept traditionally seen as exclusive to validators in PoS systems. With Berachain’s PoL, liquidity providers can stake assets without locking them up, ensuring that liquidity is constantly available for transactions, trading, and other decentralized finance (DeFi) activities. This liquidity-first approach is pivotal to the network’s scalability and efficiency.
Additionally, Berachain’s PoL mechanism addresses a long-standing issue in crypto ecosystems: the misalignment between network security and liquidity provisioning. While traditional systems separate these functions, PoL merges them, creating a more cohesive and mutually beneficial environment. By allowing liquidity providers to earn rewards while simultaneously supporting the network’s security, Berachain ensures both scalability and stability.
In essence, Berachain’s Proof of Liquidity introduces a paradigm shift in how liquidity is managed and utilized within blockchain ecosystems, making it an essential framework for the future of decentralized finance.
How Berachain Uses Proof of Liquidity
Berachain’s implementation of Proof of Liquidity fundamentally changes the way liquidity interacts with the blockchain ecosystem. Unlike traditional systems where liquidity is passively held, Berachain actively incorporates it into the security and operational structure of the network.
Here’s how PoL works within Berachain’s ecosystem:
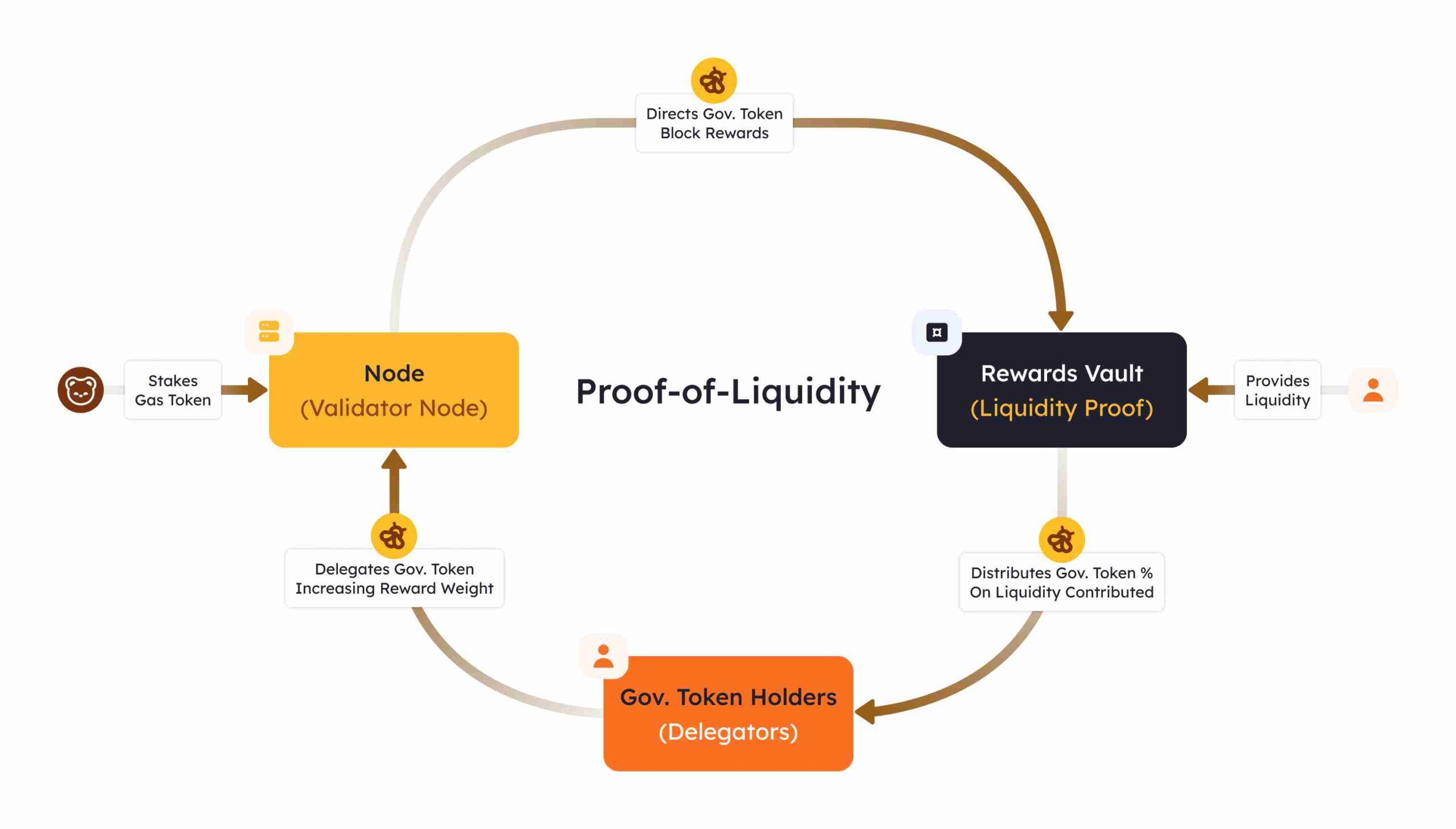
1. Staking Without Locking
Users can stake their assets without them being locked up. This enables liquidity providers to actively participate in transactions, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and lending markets, maintaining liquidity in the system. The staked assets are constantly available for use in the ecosystem, allowing them to be leveraged for other purposes, such as trading or liquidity provisioning.
2. Incentive Alignment Between Validators and Protocols
In traditional Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, there is often a mismatch between the validators (who secure the network) and the protocols (which drive ecosystem activity). Berachain resolves this by aligning the interests of both parties through Proof of Liquidity. Validators benefit from the liquidity provided by users while ensuring the security of the network. On the other hand, protocols can drive ecosystem growth and adoption by offering rewards to liquidity providers.
3. Liquidity Pools and Token Staking
Berachain’s liquidity pools are where users stake their tokens to provide liquidity. By doing so, they earn rewards not only from staking but also from their contribution to the network’s liquidity needs. These rewards come in the form of $BGT and $BERA tokens, which are critical to the ecosystem’s operation. The staked tokens back the network, providing security while still being available for use, ensuring a dynamic and active market.
4. Tokenomics and Rewards Distribution
The system works in a way that liquidity providers are continuously rewarded for their participation, contributing to the network’s liquidity and overall stability. Berachain’s tokenomics ensure that rewards are distributed fairly and equitably, promoting active participation from the community and driving the growth of the ecosystem.
5. Governance Participation
Berachain’s Proof of Liquidity mechanism also involves liquidity providers in governance decisions. By staking liquidity, users not only contribute to the network’s security but also participate in the decision-making process, ensuring a decentralized governance structure where all stakeholders have a say.
Through these mechanisms, Berachain creates a fluid ecosystem where liquidity is constantly available and network security is guaranteed. This balance between security, liquidity, and decentralization is key to its future scalability and success as a decentralized finance platform.
Bottom Line
Proof of Liquidity (PoL) represents a groundbreaking shift in decentralized finance by seamlessly integrating liquidity provision with network security. By enabling users to stake assets without locking them, PoL ensures liquidity is always available, driving efficiency and stability across the ecosystem. As a pioneer in this field, Berachain is leading the way in implementing PoL, setting a new standard for decentralized liquidity management in blockchain networks.
FAQs
1. How does Proof of Liquidity differ from Proof of Stake?
While Proof of Stake (PoS) requires locking assets to secure the network, Proof of Liquidity (PoL) allows users to stake assets without locking them. This ensures liquidity remains available for decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and other ecosystem activities.
2. Why is liquidity so important in blockchain ecosystems?
Liquidity ensures that assets can be traded easily without causing significant price fluctuations. It’s essential for the smooth functioning of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and promotes market stability.
3. How does governance work in Berachain’s Proof of Liquidity model?
Liquidity providers in Berachain’s ecosystem participate in governance by staking their assets. This gives them a say in network decisions, ensuring a decentralized and community-driven governance structure.
4. Can staked assets in Proof of Liquidity still be used for trading?
Yes, in PoL mechanisms like Berachain’s, staked assets remain liquid. Users can leverage these assets for trading, lending, or other DeFi activities while still securing the network.
5. What blockchains use Proof of Liquidity?
Currently, Berachain is a leading blockchain implementing Proof of Liquidity (PoL) as its core consensus mechanism.