Layer 1 blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Cardano form the backbone of decentralized networks. However, they often face critical challenges, including scalability issues, slower transaction speeds, and higher costs, especially during periods of high activity. These limitations have hindered their ability to meet growing demands efficiently.
To address these problems, Layer 2 solutions emerged as innovative technologies designed to enhance the performance of Layer 1 blockchains without altering their core structures. By operating as extensions or secondary layers, these solutions provide faster transaction processing, lower fees, and greater scalability while preserving decentralization.
But what exactly are these Layer 2 solutions, and how do they tackle these challenges? In this article, we’ll explore their mechanisms, benefits, and role in advancing blockchain technology.
What Are Layer 2 Solutions and Their Types?
Layer 2 solutions are designed to address the scalability, speed, and cost challenges faced by Layer 1 blockchains. These solutions function as an additional layer that operates on top of the main blockchain while maintaining its security and decentralization. Here are the main types of Layer 2 solutions:
1. State Channels
State channels create a private communication channel between participants to conduct off-chain transactions. Only the initial and final states of the transaction are recorded on the main blockchain, reducing congestion and transaction fees. Examples include Bitcoin’s Lightning Network and Ethereum’s Raiden Network.
2. Plasma
Plasma chains are separate blockchains that run parallel to the main chain (Layer 1) and interact with it periodically to enhance scalability. They enable the processing of large volumes of transactions off-chain while only submitting periodic proofs to the main chain. An example is the OMG Network.
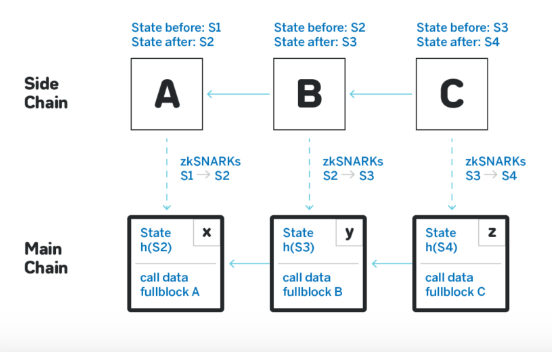
3. Rollups
Rollups bundle multiple transactions into a single batch and process them off-chain, while a summary of these transactions is posted on the main blockchain. There are two types of rollups:
Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid by default and only run fraud proofs if disputes arise (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism).
Whereas Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK Rollups) use cryptographic proofs to verify the validity of transactions, ensuring faster and more secure processing (e.g., StarkNet, zkSync).
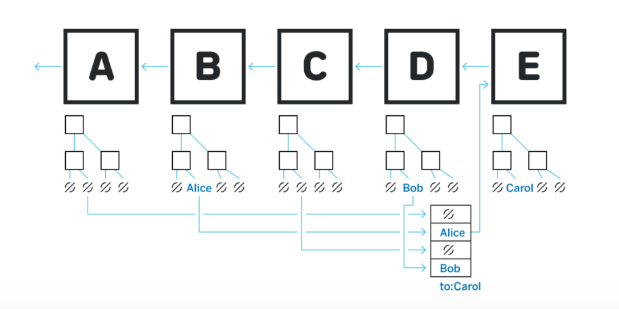
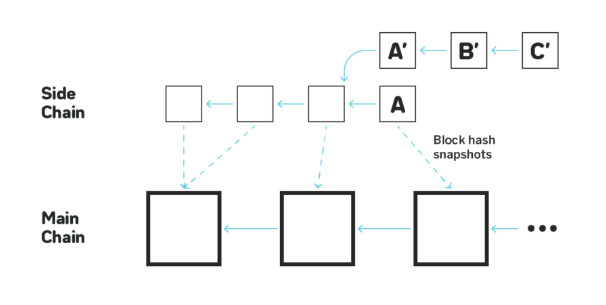
4. Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains connected to the main chain via a two-way bridge. They handle their own consensus mechanisms, allowing for faster transactions and greater flexibility. Examples include Polygon (formerly Matic) and xDai.
5. Nested Blockchains
Nested blockchains involve a hierarchy where a parent blockchain (Layer 1) oversees and secures multiple child blockchains (Layer 2). The child chains handle transactions and periodically submit data to the parent chain for finalization. An example is the Loom Network.
Importance of Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions play a vital role in enhancing the performance and usability of blockchain networks. As blockchain adoption grows, issues like slow transaction speeds, high costs, and network congestion have become significant challenges for Layer 1 blockchains. Layer 2 solutions address these limitations without compromising the security and decentralization of the underlying network.
1. Improved Scalability: Layer 2 solutions allow blockchain networks to handle a much larger number of transactions by processing them off-chain or on parallel systems. This significantly reduces the workload on the main blockchain, making it more scalable.
2. Cost Efficiency: By moving transactions off the main chain, Layer 2 solutions reduce the high gas fees typically associated with blockchain networks. This makes blockchain technology more accessible and affordable for everyday users.
3. Enhanced Speed: With faster transaction processing on Layer 2 networks, users experience quicker confirmation times. This improvement is essential for applications like payments and decentralized finance (DeFi), where delays can hinder usability.
4. Interoperability: Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups and sidechains, enable better interaction between different blockchain networks. This creates a seamless experience for users and developers, facilitating the growth of interconnected ecosystems.
5. Flexibility for Developers: Layer 2 platforms provide developers with the tools to build custom solutions tailored to specific use cases. This allows for innovation in areas like gaming, supply chain, and decentralized applications (dApps) without overburdening the main blockchain.
6. Optimized Resource Usage: By utilizing Layer 2 solutions, the main blockchain can focus on critical functions like maintaining consensus and security. This division of labor leads to a more efficient and robust ecosystem.
Bottom Line
Layer 2 solutions are all about making blockchain networks faster, cheaper, and more scalable. By handling transactions off-chain or on separate layers, they help reduce fees, speed things up, and improve overall performance, all while keeping security and decentralization intact. They’re key to unlocking more widespread use of blockchain technology and fostering innovation.
FAQs
1. What is the biggest challenge in blockchain?
Blockchain performance is affected by numerous factors, such as decentralization, security, governance models, storage and hardware requirements. However, scalability stands out as the primary challenge for developers in the blockchain space.
2. What are some real-world use cases of Layer 2 solutions?
Layer 2 solutions are used for fast payments (Lightning Network), DeFi applications (Arbitrum, Optimism), gaming platforms (Polygon), and large-scale data storage solutions like Plasma chains.
3. How do Optimistic Rollups differ from ZK Rollups?
Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid unless proven otherwise through fraud proofs. In contrast, ZK Rollups use cryptographic proofs to verify all transactions upfront, ensuring higher security and faster finality.
4. What are some real-world use cases of Layer 2 solutions?
Layer 2 solutions are used for fast payments (Lightning Network), DeFi applications (Arbitrum, Optimism), gaming platforms (Polygon), and large-scale data storage solutions like Plasma chains.
5. How do Layer 2 solutions affect blockchain decentralization?
While Layer 2 solutions enhance performance, some may compromise decentralization by introducing elements like central validators or custodians. However, hybrid models aim to balance decentralization with efficiency.




![How to Change Language in Rabby Wallet [2025 Guide]](https://www.cryptowinrate.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/How-to-Change-Language-in-Rabby-Wallet-2025-Guide-1024x576.jpg)