The term Layer 0 might sound like a new concept, but you’d be surprised to learn that this foundational layer has actually existed long before many blockchain innovations we know today. It has played a critical role in maintaining the stability and strength of blockchain infrastructure. While the terminology is relatively new, introduced as an umbrella term to define this fundamental layer, the concepts behind Layer 0 are far from recent. In this article, we’ll explore more on what exactly is Layer 0, its key functions, and how it operates within the blockchain ecosystem.
Understanding Layer 0 Protocols
To begin clearing up any misconceptions about Layer 0, let’s start with a simple explanation: Layer 0 is essentially the foundational layer of blockchain technology, sitting below Layer 1 protocols like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Cardano. It acts as the connecting framework that links different blockchain networks, enabling them to communicate and work together seamlessly.
In simpler terms, Layer 0 is a protocol that provides cross-chain interoperability, allowing different blockchain systems to interact with each other. It serves as an alternative to traditional smart contracts by supporting a broader range of use cases, such as data validation, setting reward structures, and even digital currency wrapping.
How Does It Work
Layer 0 protocols form the foundational infrastructure that powers blockchain networks. Think of it as the base of a multi-layered cake, where all the upper layers (like Layer 1 and Layer 2) rely on this foundation to function effectively. Layer 0 provides the essential framework for blockchains, including protocols, consensus mechanisms, and network design. This ensures the smooth operation of blockchain ecosystems by enabling communication, data storage, and security at the most fundamental level.
A key feature of Layer 0 is its ability to connect different blockchains. Traditionally, blockchains operated like isolated islands, unable to share information with one another. Layer 0 changes this by introducing protocols like cross-chain bridges, allowing data and tokens to move seamlessly between blockchains. For instance, it enables users to transfer assets between Ethereum and Bitcoin effortlessly.
To optimize blockchain structure, Layer 0 supports various technologies, including advanced consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Work (PoW). Additionally, it employs innovative designs such as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to enable efficient and scalable data validation. At a technical level, Layer 0 also uses state channels to validate and transfer data according to predefined rules, while nodes—devices or computers connected to the network—ensure the system’s integrity and security.
Lastly, Layer 0 relies on native tokens to incentivize user participation. Validators and participants are rewarded with these tokens for contributing to the network’s operations, fostering a balanced and sustainable ecosystem. By combining these features, Layer 0 provides the robust foundation necessary for blockchain innovation and interoperability.
Key Features of Layer 0 Blockchains
Layer 0 blockchains are the foundational layer of decentralized networks, offering unique capabilities that enhance the performance, security, and scalability of blockchain ecosystems. Below are the key features that set Layer 0 apart:
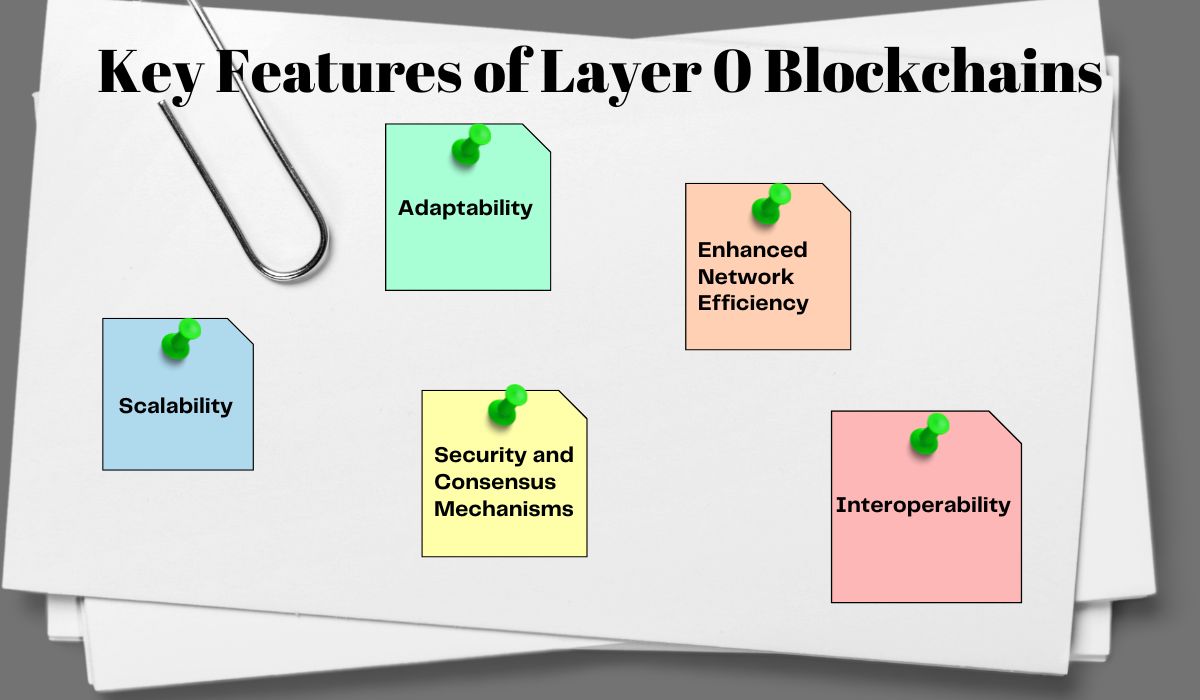
1. Scalability
One of the primary advantages of Layer 0 is its ability to address scalability issues faced by earlier blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Techniques such as sharding, where the network is split into smaller partitions for parallel transaction processing, enable significantly higher throughput. This ensures the network can handle increased transaction volumes without congestion or delays.
2. Interoperability
Layer 0 protocols foster seamless communication between different blockchains. They use technologies like cross-chain bridges and interoperability frameworks to allow data and assets to move across networks. For example, a Layer 0 protocol could enable a decentralized finance (DeFi) application on Ethereum to interact with a supply chain solution on Polkadot.
3. Security and Consensus Mechanisms
At its core, Layer 0 ensures the security of the entire blockchain system by incorporating advanced consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS). These mechanisms rely on economic incentives to maintain a trustless and tamper-proof environment, making it difficult for malicious actors to compromise the network.
4. Adaptability
Layer 0 supports multiple consensus algorithms and network designs, making it highly adaptable to the needs of different blockchain projects. Developers can customize the foundational architecture based on specific use cases, whether they need high-speed transactions, decentralized governance, or privacy-focused solutions.
5. Enhanced Network Efficiency
By optimizing network topology and using technologies like Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), Layer 0 achieves faster data validation and more efficient resource utilization. This helps reduce transaction costs while maintaining high network performance.
Examples of Layer 0 Protocols
Let’s take a look at some popular layer 0 protocols that are currently providing value within the blockchain industry:
Polkadot
Polkadot, a well-known Layer 0 protocol, uses a central “Relay Chain” to connect multiple individual blockchains called parachains. Each parachain can operate independently but communicates efficiently through the Relay Chain. This setup allows developers to create custom blockchains while benefiting from Polkadot’s security and interoperability features.
Cosmos
Cosmos is designed to enable communication between independent blockchains through its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. It consists of the Cosmos Hub, which acts as a central ledger, and customizable Zones, where developers can build their blockchains with unique configurations. Each Zone benefits from shared security provided by the Cosmos Hub while maintaining independence. The platform focuses on interoperability, scalability, and developer flexibility.

Avalanche
Avalanche features a tri-blockchain structure comprising the Exchange Chain (X-Chain) for asset creation, the Contract Chain (C-Chain) for smart contracts, and the Platform Chain (P-Chain) for network coordination and validation. This structure ensures low latency, high throughput, and efficient cross-chain communication. Launched in 2020 by Ava Labs, Avalanche is widely used for decentralized finance (DeFi) and asset trading while supporting customizable blockchain creation.
Substrate
Substrate, developed by Parity Technologies, serves as a modular framework for building blockchains. It powers blockchains such as Polkadot and enables developers to create customized networks with built-in interoperability features. Substrate offers pre-designed modules for consensus mechanisms, governance, and other essential functionalities, simplifying the process of blockchain development. Its flexibility and integration capabilities make it a preferred choice for Layer 0 infrastructure.

Road Ahead
Layer 0 protocols are set to play a transformative role in the evolution of blockchain technology. As the demand for scalability, interoperability, and customization continues to grow, these foundational protocols will shape the next generation of decentralized applications and ecosystems. By addressing key limitations of earlier blockchain layers, Layer 0 enhances performance while opening new avenues for innovation across industries.
However, challenges such as achieving standardization across different Layer 0 protocols and ensuring strong security against emerging threats remain critical. The future of blockchain lies in creating an interconnected and scalable ecosystem, with Layer 0 playing a central role in driving this transformation. As these protocols continue to evolve, they will create significant opportunities for decentralized innovation, enabling industries to fully leverage blockchain technology in meaningful ways.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Layer 0 and Layer 1 protocols?
Layer 0 protocols serve as the foundational infrastructure for blockchain networks, enabling cross-chain interoperability and scalability. In contrast, Layer 1 protocols like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate as standalone blockchains, focusing on transaction processing and consensus mechanisms within their individual ecosystems.
2. How does Layer 0 improve blockchain interoperability?
Layer 0 achieves interoperability by providing cross-chain communication protocols, such as cross-chain bridges, which allow data and tokens to move seamlessly between independent blockchains. This enables different blockchain networks to interact and work together efficiently.
3. Can Layer 0 protocols replace smart contracts?
Layer 0 protocols do not replace smart contracts but complement them by providing enhanced scalability, interoperability, and broader use cases. They offer foundational capabilities that expand the potential of decentralized applications (dApps) built on Layer-1 or Layer-2 networks.