Reviews, Comparisons, Guides & Research
Everything you need to know about Crypto!
Read reviews, comparisons, and guides about crypto exchanges, wallets, and cryptocurrencies to get ahead of the market.

Crypto Exchange Reviews
If you are not sure yet which crypto exchange is best for you, you can dive deep into the best crypto exchanges in the world. We have done the work and tested over 100 cryptocurrency exchanges. We have you covered with absolutely everything you need to know, including security, features and products, fees, assets, restrictions, requirements, and much more.
Before you register on any of these platforms, we highly recommend you read our in-depth crypto exchange reviews. Our analysts are putting in countless of hours to update the reviews at CryptoWinRate on a daily basis.
| Exchange | Established | Users | Spot Coins | Futures | Spot Fees | Futures Fees | Max Leverage | Bonus | KYC | Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Bitunix | 2022 | 3+ million | 317+ | 218+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
125x | $5,500 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 2. Blofin | 2019 | 2+ million | 394+ | 329+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
150x | $5,000 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 3. BYDFi | 2019 | 4+ million | 418+ | 187+ | Maker: 0% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
200x | $300 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 4. Bybit | 2018 | 30+ million | 660+ | 386+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.055% |
100x | $30,000 | Required | Read Review |
| 5. BTCC | 2011 | 3+ million | 88+ | 309+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.045% |
500x | $11,000 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 6. Bitget | 2018 | 8+ million | 871+ | 246+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
125x | $20,000 | Required | Read Review |
| 7. WEEX | 2017 | 5+ million | 462+ | 396+ | Maker: 0% Taker: 0% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
200x | $241 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 8. MEXC | 2018 | 6+ million | 3137+ | 433+ | Maker: 0.05% Taker: 0.05% |
Maker: 0% Taker: 0.02% |
300x | $20,000 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 9. Binance | 2017 | 213+ million | 414+ | 352+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.05% |
125x | $100 | Required | Read Review |
| 10. BingX | 2018 | 5+ million | 824+ | 246+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.05% |
200x | $5,000 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 11. Phemex | 2019 | 5+ million | 355+ | 260+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.01% Taker: 0.06% |
100x | $8,800 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 12. Zoomex | 2021 | 3+ million | None | 220+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.06% |
100x | $100 | No KYC | Read Review |
| 13. Coinbase | 2012 | 108+ million | 250+ | 10 | Maker: 0.4% Taker: 0.6% |
Maker: 0.05% Taker: 0.05% |
10x | None | Required | Read Review |
| 14. Bitvavo | 2018 | 2+ million | 308+ | 0 | Maker: 0.15% Taker: 0.25% |
Maker: 1% Taker: 1% |
1x | $10 | Required | Read Review |
| 15. OKX | 2017 | 50+ million | 317+ | 207+ | Maker: 0.08% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.05% |
125x | $10 | Required | Read Review |
| 16. LBank | 2015 | 7+ million | 1500+ | 100+ | Maker: 0.1% Taker: 0.1% |
Maker: 0.02% Taker: 0.05% |
100x | None | Required | Read Review |
Best Crypto Wallets
Not your key, not your cryptos! If you are not sure which cryptocurrency wallet is best for you, read our detailed reviews about top crypto wallets. We cover everything you need to know about the best hardware and software wallets in the industry.
Crypto Guides
Read in-depth guides about everything crypto! Our team has carefully crafted detailed step-by-step tutorials about various topics, which you can easily follow along. Learn about bridging, adding tokens to wallets, depositing and withdrawing on crypto exchanges, and much more.
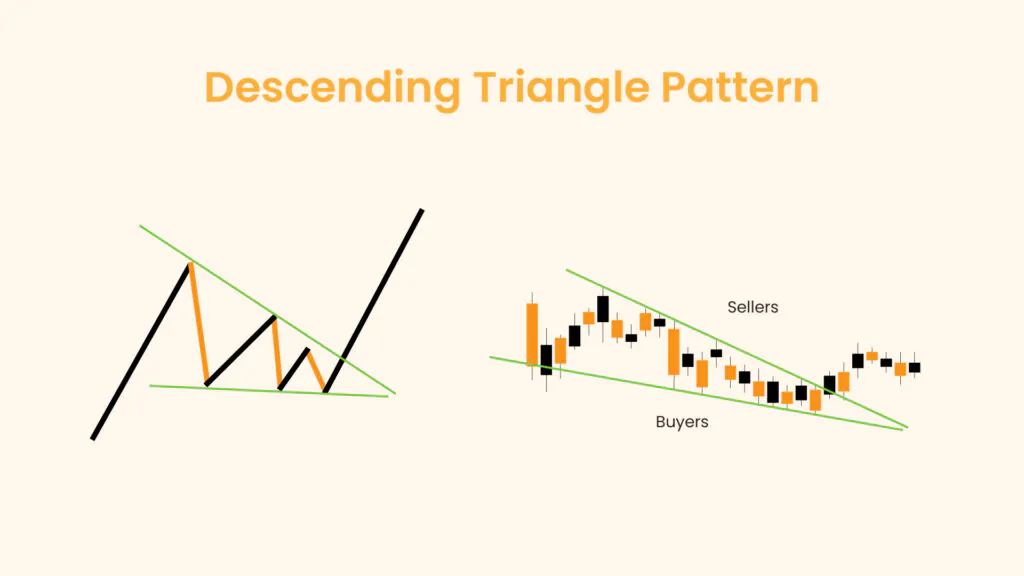
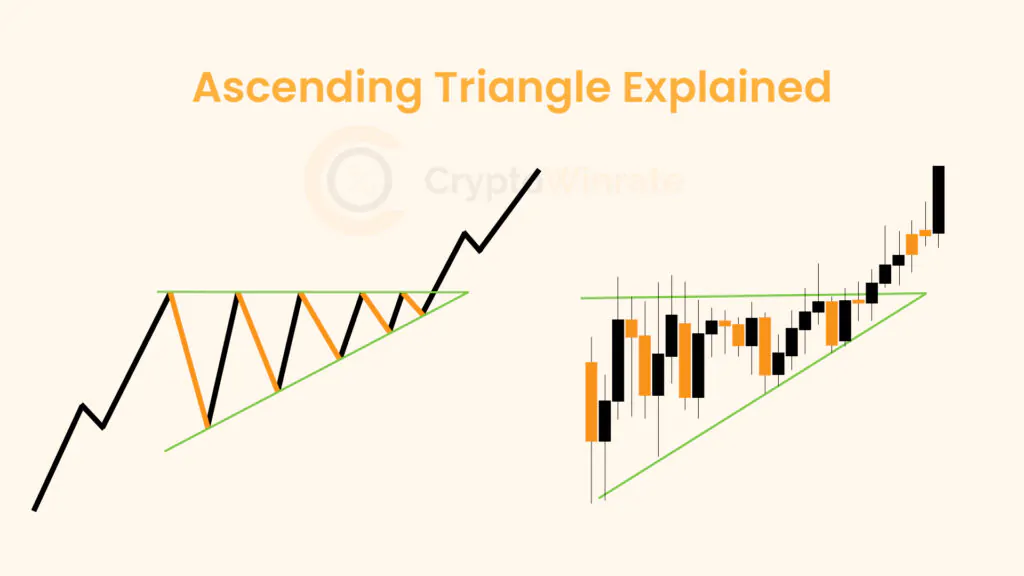
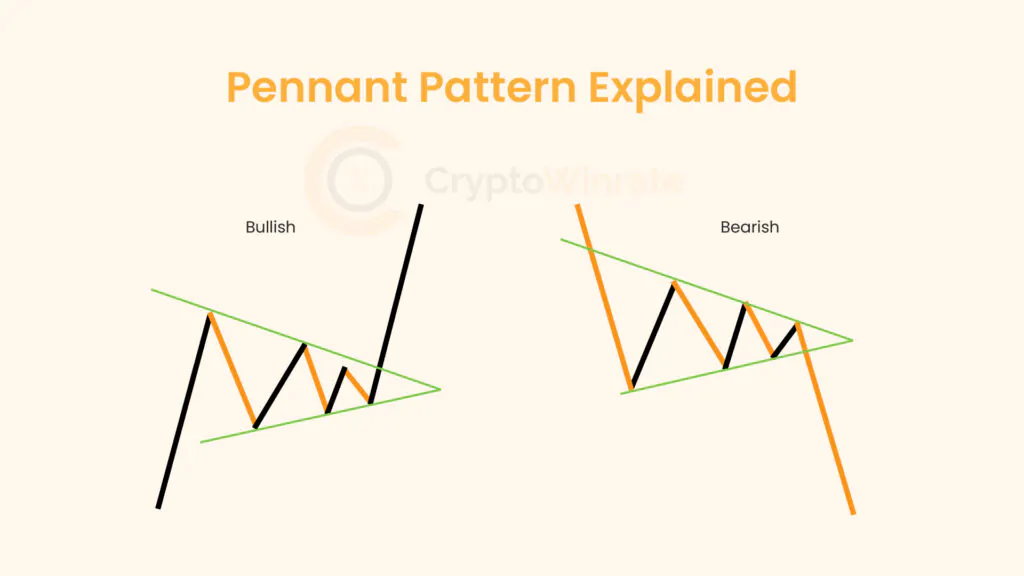
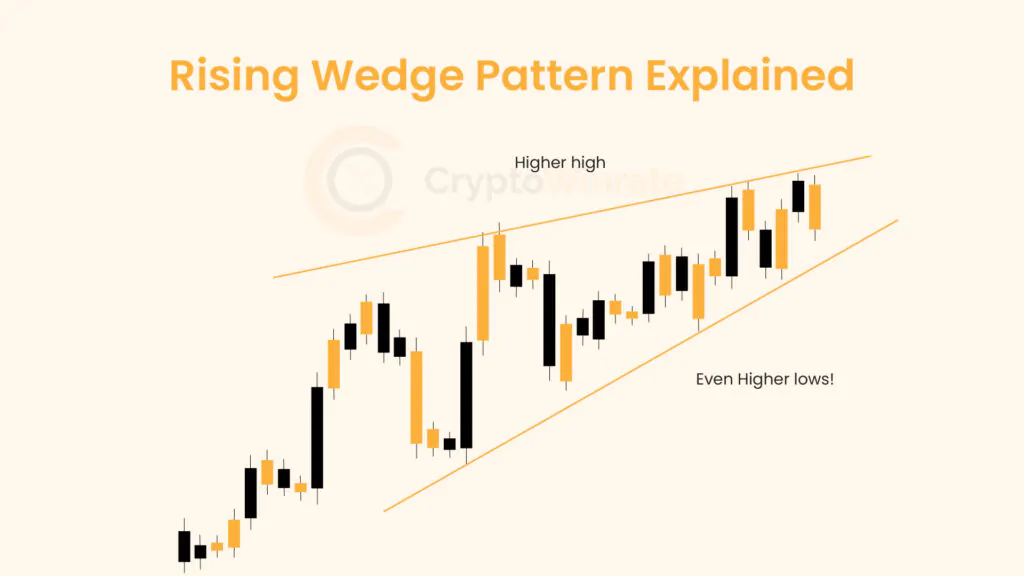
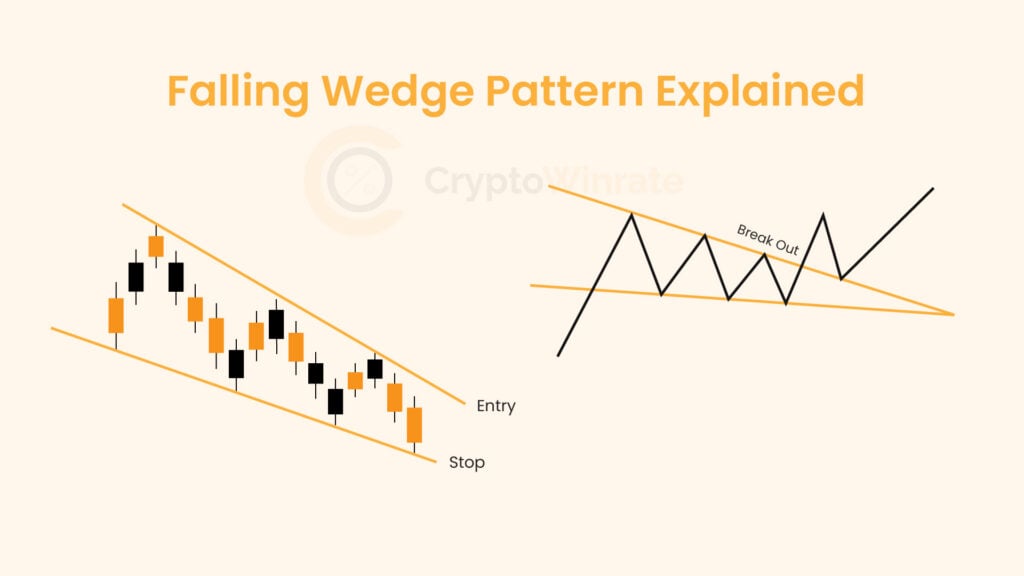
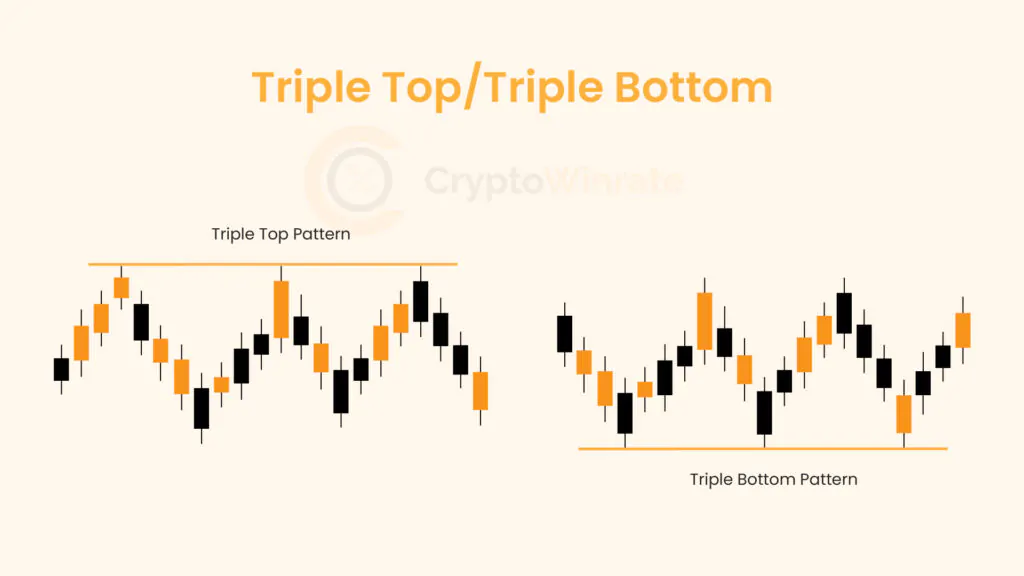
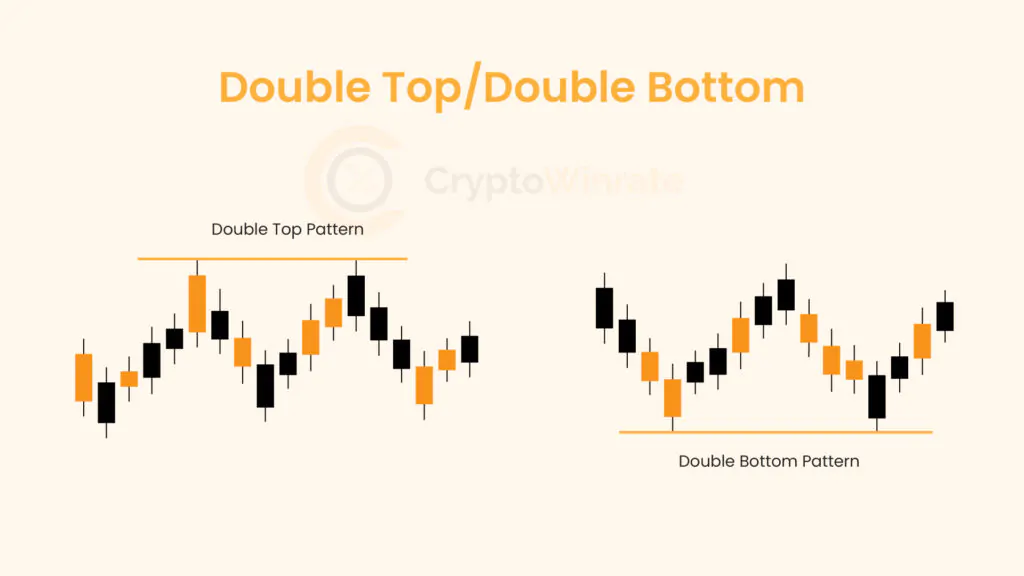
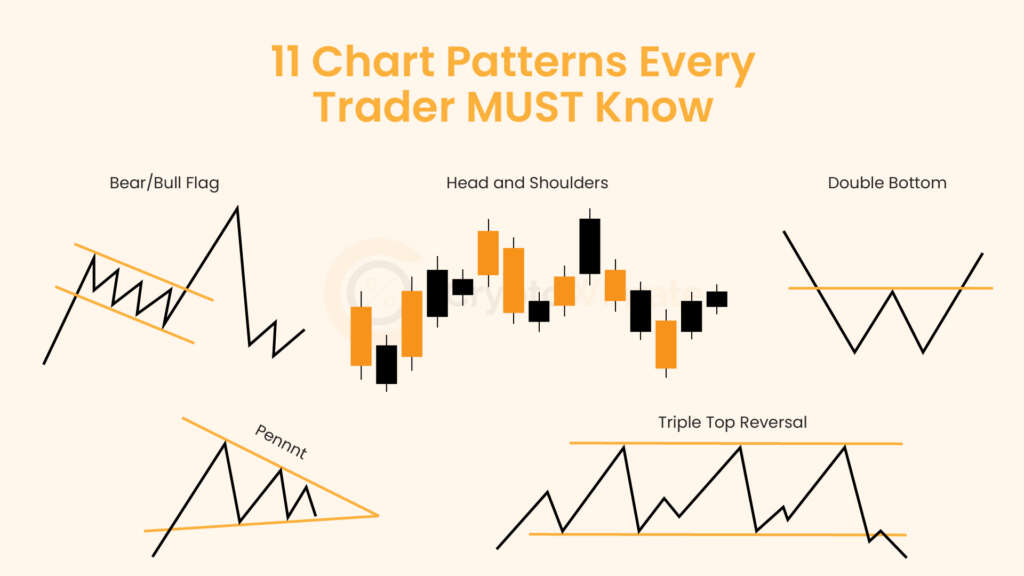
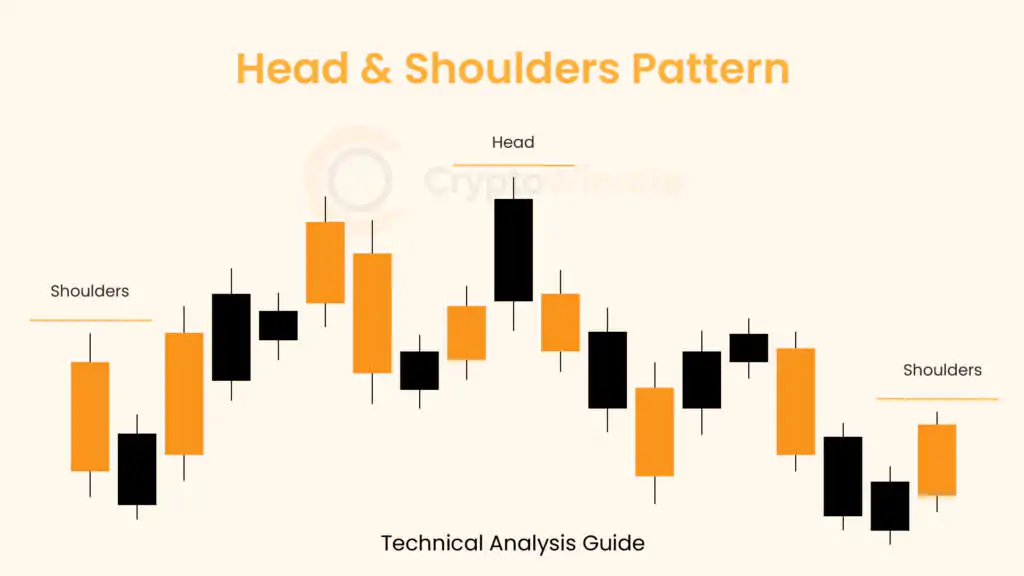
Technical Analysis
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your technical analysis skills, our educational resources will help you develop a stronger foundation for your trading strategy.
Browse through our carefully curated articles and take your trading knowledge to the next level. Learn about chart patterns, trading, and technical analysis.
Best Crypto Exchanges & Trading Platforms 2025 List
On cryptowinrate.com, you will not find reviews from researchers but from actual traders who have experience in the market. We have thoroughly tested and reviewed over 150 crypto trading platforms. If you are looking for a review of a specific exchange, you can search for it in the search bar above.
Below, you will find a quick overview of our top Cryptocurrency exchanges for 2025. We went through all the important details, which you can find in the full review. Scroll through and see what suits your needs best!

Features
- 400+ Supported cryptos
- Trade with low fees and deep liquidity
- Advanced copy trading feature
- No KYC required (anonymous trading)
- Very user-friendly
- $5,500 Trading Bonus
- 10% Fee Cashback
Supported Cryptos
400+
Max. Leverage
125x
Maker/Taker Fees %
0.02/0.06
UI Stability

Features
- 390+ Supported cryptos
- Trade with low fees and deep liquidity
- Advanced copy trading feature
- No KYC required (anonymous trading)
Supported Cryptos
390+
Max. Leverage
150x
Maker/Taker Fees %
0.02/0.06
UI Stability

Features
- The only exchange with 0% maker fees on futures and spot markets
- Passive income with an advanced Copy trading network
- Invest and trade crypto without KYC (anonymous)
- 200x highest futures trading leverage
Supported Cryptos
2100+
Max. Leverage
200x
Futures Maker/Taker Fees %
0/0.02
UI Stability
Features
- Crypto derivatives with deep liquidity
- Vers user-friendly & reliable User Interface
- Low fees and low spread for spot and futures trading
- Designed for experienced and beginner traders
Supported Cryptos
650+
Max. Leverage
100x
Maker/Taker Fees %
0.02/0.055
UI Stability

Features
- Beginner friendly derivatives exchange
- Advanced Copy Trading
- Invest and trade crypto with low fees
- Euro Deposit & WIthdrawals supported
Supported Cryptos
680+
Max. Leverage
125x
Maker/Taker Fees %
0.02/0.06
UI Stability

Features
- Largest Crypto Exchange in the World
- Most advanced features, products & services
- Low fees and deep liquidity on spot and futures
- Designed for experienced traders only
Supported Cryptos
350+
Max. Leverage
125x
Maker/Taker Fees %
0.02/0.05